RE: Rewards For Recycling
owners to foster a sustainable world through recycling initiatives
Recycling Application assisting Millennials and Business
.png)


Overview
RE: Rewards For Recycling is a mobile application designed to encourage recycling practices. It aids the users in identifying recyclable items for proper disposal, provides guidance on recycling regulations within the community, and offers rewards to users who maintain consistent recycling habits. In the application, users can establish recycling goals and track their environmental impacts. Businesses and communities have the opportunity to encourage sustainable habits through recycling initiatives by creating challenges and offering local incentives for individuals to redeem, fostering a collective community endeavor.
Role: UX Researcher/ Interaction Designer / UI Designer
Duration: 16 weeks
Skills: Interviewing / Survey Design / Competitive Analysis / Wireframes /
Prototyping / User Testing
Tools: Figma/ Google Forms/ Adobe Premiere Pro
The Problem
North America is home to less than 5 percent of the global population but generates 14 percent of the world’s waste. In the US, individuals generate nearly 5 pounds of waste per day per person and Americans collectively recycle only 32% of materials that could be disposed of in traditional, municipal-level recycling schemes. When Americans do attempt to recycle, contamination—the mixing of recyclables with non-recyclables—often renders the materials too costly to sort and make new products from.

United States contributes 14% of world's waste
The Opportunity
Many Americans are interested in changing their behaviors and adopting a more sustainable lifestyle if they are armed with accurate information and have options available. In fact, some have already taken measures to be more eco-conscious consumers, with about 38% of consumers saying sustainable packaging is “extremely” or “very” important to their purchasing decisions. Although price ranks much higher than packaging or environmental concerns as a decision-making factor in consumers’ minds, 60 to 70 percent of consumers say they would pay more for sustainable packaging. Studies show that Americans who fall into the generational cohorts of “Millennials” and “Generation Z” are most interested in and likely to adopt new behaviors related to a sustainable lifestyle.

92% of Americans are confused about recycling labels and rules
1 McKinsey & Company’s 2020 Report, “Sustainability in packaging: Inside the minds of US consumers.”
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/paper-forest-products-and-packaging/our-insights/sustainability-in-packaging-inside-the-minds-of-us-consumers

Exploratory Research
Interviews
Based on our preliminary exploration into the problem space of recycling and sustainable living, we envisioned our potential user base could fall into one of three categories: individuals with an interest in sustainability, local businesses with values in sustainability, and municipality waste management officials.
Following our interviews, our scope was refined to focus on individual consumers as the end users responsible for sustainability-related decisions. Our initial objectives for our solutions revolved around raising awareness of recycling, providing educational resources on sustainable practices, and motivating users to adopt sustainable behaviors.

Millennials 22-35 years of age with an interest in sustainable lifestyle
.png)
Eco Friendly Businesses

Municipality Waste Management Officials
We conducted a total of 7 interviews. We recruited participants from two main user groups: Millennials and Experts. I lead interviews with a local zero-waste BYOC business owner and a millennial interested in sustainable practices. Through these interviews, I was able to learn that although individuals are interested in being sustainable there are often barriers and gaps of knowledge preventing individuals from continuing these practices. It was found commonly between business owners' and municipality officials' opinions that it was up to businesses and communities to aid in pushing individuals towards sustainable efforts through means of educating and making efforts feasible.
Thinks businesses have a huge part to play in re-use and recycling effort.
P01:
Most frequent question they are asked is how to recycling plastics bags, bubble wrap, plastic film, etc
P02:
"For a lot of people [reduce/reuse/ recycling] is not financially feasible, like alternative milk or avoiding plastics can be expensive"
P03:
Would be easier to work towards waste reduction if recyclables were easily identifiable and knowing where to find zero waste products.
P07:
Key Findings
-
People commonly are concerned about the cost of living sustainably.
-
A common source of frustration arises from understanding how to properly divert different types of plastic.
-
Individuals are motivated by friends, their wallets, and by seeing tangible impacts, both positive and negative.
-
The best way to reach consumers is through working with businesses, institutions, and governments.
Exploratory Research
Competitive Analysis
To supplement our research, our team looked into other ways existing mobile applications and websites in the sustainability space operate. We conducted a competitive analysis, and output data into a matrix. We analyzed apps’ and website details, target markets, key user tasks, and features. Through this analysis, we were able to understand how users were incentivized, how they engage with the rest of the app’s and website user base, and how gamification could be implemented into a product.

Competitive Matrix Findings
We were able to learn that our primary competitors were Recyclebank and zeLoop. Recyclebank partners with cities to provide redeemable points for recycling, while zeLoop offers rewards to individuals for documenting their items and depositing recyclables at recycling centers. However, Recollect served as our indirect competitor, focusing on B2B and educating users on recycling.

Insights

Bespoke Solutions: Lack of integration with other technologies.

No voice interface components

Action-oriented products focus on environmental impacts or monetary rewards
.png)
Any personalization is based on user's locations

Gamified products use points, tokens, and leaderboards

For gamified products, verification for points can use self-verified technology

For some products, the municipality must choose to be involved

Both municipality-level technology focus on education
Exploratory Research
Target Users
From our interviews, matrix, and initial research findings, we were able to identify our target audience; millennials 22-35 trying to live a sustainable lifestyle, who would be the demographic for our product, and moved to what their primary goals may be from using it; reusing & and recycling with means of motivation. We created two personas and scenarios at this stage.
Exploratory Research
Ideation
Using our personas we created three initial concepts with our MVP (minimum viable product) features we gathered through analyzing our competitive matrix and interviews.
MVP Features
Item identification through mobile app
Options for waste diversion based on the item (e.g. recycle, reduce, buy a different product)
Rewards for completing actions to divert waste
Specific focus on plastics and packaging
Community engagement/forum
Engagement with eco-conscious businesses and institutions
Concept 1: Recycling Market
It is a mobile application to promote the reuse and recycling efforts through a marketplace. It identifies the product by taking a picture, and related information is provided about the proper disposal method along with recommendations for alternative eco-friendly products. Users can keep track of their recycling impacts and earn points for disposing. Users can redeem points to earn coupons to buy eco-friendly products through the marketplace to increase awareness of local businesses participating in the initiative. Businesses can add additional points for closed-loop cycles. Community forums for users to share information on reducing and reusing.


Concept 2: Plastic Hacker
Community-sourced hacks for reducing, reusing, and recycling plastics with emphasis on cost savings. Search for hacks by typing in using voice assistants, or taking a picture. Post your own hacks with descriptions, photos, and tags. Earn points by completing hacks in your to-do lists and getting upvotes from the community. Use points for rewards through partnerships with businesses and municipalities. Integrate with social media such as Pinterest.


Concept 3: Smart Recycle
Mobile application that scans the barcode of an item, displays information about the product, and how to properly dispose. Find a nearby waste bin with wifi + Bluetooth enabled (similar to Airdrop). Points earned for disposing. Community forum to discuss questions about recycling locations, materials, etc.


Formative Research
Surveys
During this phase of the project, our team aimed to focus our scope on one of the three waste diversion stages. We wanted to learn through our survey where we could provide users the most value to promote a sustainable lifestyle and identify ways to motivate users toward this cause. We aimed to learn about users' challenges and behaviors related to waste management. In addition, within the survey to assess desirability, we added two low-fidelity project concepts, one focused on user reusing and the other towards recycling. We requested survey participants to select three words that best represented their feelings towards the concepts and offered the opportunity to join our in-person desirability study. We created our survey through Google Forms and recruited individuals through channels of Slack and Facebook.
Overarching Questions
At what phase of waste diversion ( reducing, reusing, or recycling) can our product provide the most value to users?
How should our product incentivize users to divert waste?
How would users like to interact with our product and/or each other?
Age 22-35
"Somewhat" to "Very" interested in adopting more sustainable behaviors at home
Lived in off-campus housing
Survey Criteria:

Survey Results
We received 46 out of 54 eligible responses fitting within our criteria. We were able to validate our findings from the exploratory stage and learn about potential user behaviors, motivation and challenges.
Behaviors
Users “always” or “often” recycle and most often have access to curbside recycling.
They already attempt to re-use or re-claim items through existing apps and services.
Pain Points
Users are confused about what and how to recycle, citing perplexing labels and differing regulations by city and state.
Single-use plastics and plastic films/packaging cause the most frustration for users.
Time commitment is the most significant barrier to reusing and recycling properly
Users aren’t aware of options for recycling items that can’t go in curbside pick-up.
Affordability is a barrier to more sustainable product purchases.
Motivation
Users want to see the environmental impact of their behaviors.
Users are motivated by direct rewards, such as discounts or freebies, particularly at local and environmentally-conscious businesses.

Formative Research
Desirability Testing
In preparation for our desirability test, we chose to refine and improve our three initial concepts before proceeding to our testing phase. We combined Concept 1: Recycling Market and Concept 3: Smart Recycle together as they were similar to test against Concept 2: Plastic Hacker. In our study, we aimed to (1) assess the usefulness of each prototype and specific features in the eyes of our target users, (2) determine which prototypes, illicit feelings of motivation or inspiration, and (3) gauge users’ understanding of how each prototype works.
Participants were shown the two low-fidelity concepts and asked to select the three words from a predetermined list of adjectives that best describe how they feel about the concepts. The study was conducted remotely with 46 participants alongside the survey and 2 in-person studies were performed.
Concept 1
Take a photo of a plastic item and see crowd-sourced "hacks" for reusing it. Earn points by completing hacks in your to-do list and posting new hacks that other users upvote.

Concept 2
Scan the barcode of any item and see how and where to recycle it. Earn points by recycling properly and see options to redeem points for rewards.

Desirability Findings
Both concepts were “clear”, “understandable”, and “useful.” However, Concept 2 was far more “motivating” for users, and as the in-person tests revealed this was because of the ability to see the direct connection between recycling a product and receiving a reward. Additionally, one user noted that she thought Concept 1 was “ineffective” because she “didn’t have time to make DIY projects.” With Concept 2 outperforming Concept 1, at this stage, we made the decision to move forward with this idea.

The Problem Statement
Many young adults between the ages of 22-35 residing in major cities across the United States express an interest in adopting a more sustainable lifestyle. They actively participate in recycling at home and have the convenience of single-stream curbside collection services. However, they often face frustration due to unclear recycling regulations specific to their area and struggle to dispose of items that can not be placed at the curbside. Further, even after resolving these challenges, they lack the motivation to sort and transport their items to the appropriate disposal centers. As a result, these items often end up in the recycling bin, causing contamination, or in the waste bin, ultimately with the items ending up in landfills in both scenarios.

Design Research
Prototyping
As we began to develop our mid-fidelity prototype, we created a user flow map and used our past prototypes as references as a starting point. We incorporated our core flows focusing on the acts of identifying, locating, recycling, redeeming, and supporting. We designed our basic interface elements to be tested in our usability tests.
1. Identify an item and learn how and where to recycle it.
2. Recycle the item properly and earn points.
3. Redeem points for rewards in the form of discounts and free products/services.
4. Find the answer to a recycling-related question in a community for
Core Flows
Mid-Fi Prototype
Evaluative Research
Usability Evaluation
Our objective for our usability testing was to uncover specific problems in the prototype design and interactions, improve users’ performance with core actions and flows, and identify any challenges in users’ understandability with the core flows. The participants were given 5 tasks to complete within the core flows of recycling, rewards, and community. Participants had to identify items, add items to collections, redeem points, set goals, and find information.
3 Usability Tests



Recycling
-
Identify item
-
Add item to the collection
Rewards
-
Redeem Points
-
Set goal
Community
-
Find information
Key Interactions
Usability Results
All our participants were able to complete the five tasks. However, there was some confusion and inconsistencies leading to longer recovery times for our participants. Based on the feedback and testing, we found areas of opportunity to make our prototype more intuitive, match user expectations, mitigate confusion, and decrease error recovery time
I would definitely bring my batteries and stuff to be recycled if I could get a free coffee out of it.
– Usability Testing Participant 02
"
Prototyping
Design Evolution
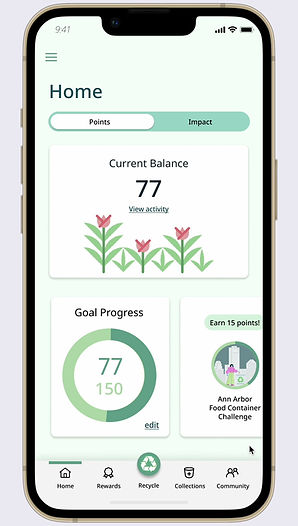
Home
Changes were made to the home screen to allow users the ability to edit and set goals. The goals show what rewards can be achieved at the chosen level, further incentivizing users. The impact page was updated to show environmental impact in relation to the target the user is aiming to achieve, rather than the community average.



The impact page was updated to show environmental impact in relation to the target the user is aiming to achieve, rather than the community average.


Recycling
The main recycling action button’s label and icon was updated to be more intuitive to users.

The option to choose to recycle at a recycling center versus saving an item to collections was more clearly distinguished and re-ordered in the flow.


Collection Center
We added a map to find recycling centers from the collections screen, as well as the option to submit curbside photos to earn points.
Rewards
The option to review rewards by point level was added to the rewards screen.
Community
Challenges were added based on feedback from participants about community-level incentives.







Prototyping
Style Guide
At this stage of our high-fidelity prototype, we made updates to our style guide to keep visual design cohesiveness.

Final Product
Key Features & Flows
Product Identification
Users identify the item to dispose of by scanning its barcode, taking a photograph, or searching for it in a robust database and a search form with a helpful autocomplete input field. Having all three options increases accessibility and makes it easier for users to determine how to recycle a product when they don’t know what materials it’s made of.
Paint Points Addressed:
Confusion about what and how to recycle.

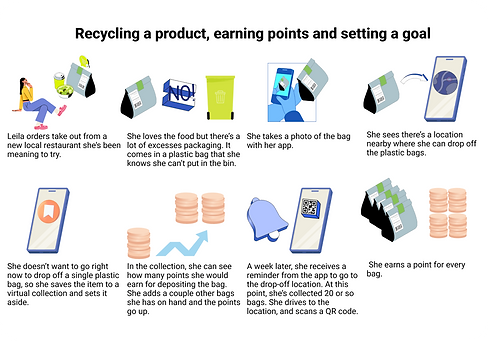
Recycle to Earn Points
For items that need to be taken to a recycling center or drop off location, the app provides nearby locations. When users arrive at the selected location, they scan a barcode to earn points. Users can also add items to virtual collections so that they can wait to go to a recycling center when they have several items to dispose of. For items that can be recycled in curbside pick-up, points are earned by taking a photo of your curbside bin on recycling day.
Motivation Mechanism:
Direct Rewards
Paint Points Addressed:
Perceived lack of options,
Time commitment
Set Goals & Track Progress
Set personal goals for points and targets for environmental impact. Progress toward goals is tracked with simple data visualizations. Point goals are set at tiers (25 points, 50 points, 75 points, 150 points) that align with reward levels, so if users know what reward they want, they can set their goal to that point level. Environmental impact indicators include items scanned, pounds recycled, and CO2 saved.
Motivation Mechanism:
Environmental Impact
Paint Points Addressed:
Perceived lack of options,
Time commitment


Redeem Points for Rewards
Users redeem points for discounts, free items, and other rewards at local and online businesses. The platform prioritizes eco-conscious businesses and sustainable products. For online rewards, users receive a discount code to use. For in-store rewards, an employee scans the QR code on the user’s phone to redeem the reward.
Motivation Mechanism:
Direct Reward
Paint Points Addressed:
Affordability, Time Commitment (Offsetting)
Engage in a Local Forum
Users can post questions, read updates from their municipality waste management division and local businesses, engage in conversation, or get information about local events in their geographically customized forum.
Motivation Mechanism:
Recognition for Actions


Compete in Local Challenges
To increase impact, earn extra reward points, and engage at a community-level, users can take part in local challenges sponsored by RE or local businesses and municipalities. Leaderboards on challenges further incentivize participation.
Motivation Mechanism:
Recognition for actions,
Environmental Impact
Value to Users
Reaching Sustainability Goals
RE helps users recycle mindfully, reducing frustration and feelings of uncertainty around how to dispose of various products. By giving users the opportunity to track their recyclables, the environmental impact they have through recycling becomes tangible.
Rewarding Follow Through
Our interviews, surveys, and desirability tests indicated that users are motivated by receiving rewards that are directly tied to an action. By tying rewards to point levels and allowing users to earn points for each action, users are motivated to follow through. For instance, if a user has a virtual collection, they can see the number of points they will earn by going to a recycling center to dispose of the collection. In the survey and in-person desirability study, we learned that users appreciate rewards at local businesses on items they regularly purchase (e.g. coffee) or on items that help further their sustainability goals (e.g. bulk detergent or zero waste deodorant). RE offers rewards that align with these user-centered incentives.
Engaging all Stakeholders
RE also engages businesses and municipalities in recycling. Businesses with eco-conscious values have a clear incentive to participate in the RE program to build credibility and expand their customer base. RE helps municipalities by disseminating information about recycling options and collection pick-up days. Reducing contamination in curbside programs will save municipalities money. Businesses and municipalities can also participate through the community forum and challenge features.
Creating a More Sustainable World
Ultimately, RE helps create a more sustainable world by providing a viable way for people in the United States to mitigate the effects of overconsumption and divert waste from landfills. By diverting waste from landfills, RE helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions that lead to climate change, conserve energy, and reduce natural resources used in creating new products from raw materials.

The Team: Safa Viqar, Mariele Ventrice & Sadhana Ramaseshadri